Precision measurements with BaF molecules
In this project, we use laser-cooled diatomic molecules as sensors for tests of fundamental symmetries.
Over the centuries, the main driving force of physics has been the search for the fundamental laws describing the workings of our universe. Key tools to achieve progress in this direction have recently been increasingly powerful, yet also increasingly complex and expensive particle accelerators and other large-scale facilities. An complementary approach in the search for new physics are compact precision experiments on much smaller energy scales. By realizing precisely controlled molecular quantum systems, measurements with extraordinary precision become possible, opening up a new window into the world of high-energy and nuclear physics.
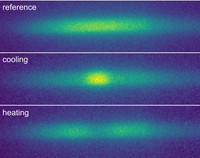
Our current molecule of choice is barium monofluoride (BaF). BaF is very heavy, which yields a high sensitivity to many fundamental effects that we want to investigate. We use buffer gas cooling and laser cooling to generate a cold and intense beam of BaF molecules for our measurements.
Recent publications:
- Laser cooled 137BaF molecules for measuring nuclear-spin-dependent parity violation
F. Kogel, T. Garg, M. Rockenhäuser, and T. Langen
Phys. Rev. Research 7, L022041 (2025), arxiv: 2501.16095 (2025) - Isotopologue-selective laser cooling of molecules
F. Kogel*, T. Garg*, M. Rockenhäuser, S. A. Morales-Ramírez, and T. Langen
New J. Phys. 27, 013001 (2025), arxiv: 2406.01569 - Laser cooling of barium monofluoride molecules using synthesized optical spectra
M. Rockenhäuser*, F. Kogel*, T. Garg, S. A. Morales-Ramírez, and T. Langen
Phys. Rev. Research 6, 043161 (2024), arxiv:2405.09427
Laser cooling of BaF molecules
Experimental Setup